Post by glactus on Feb 17, 2008 7:37:18 GMT
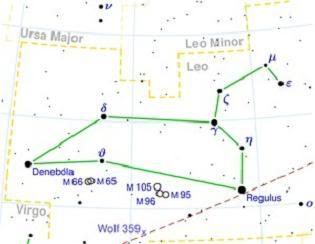
So angry was Hera at Hercules' success that she raised the soul of the lion high into the sky, where today he can be seen as the constellation Leo, the Lion. A constellation of the zodiac, Leo is one of a handful of constellations that really does look like its namesake. Look for the lion high in the sky in April and May.
Notable stars:
Alpha leo (Regulus)
Regulus, a first magnitude star, is the 21st brightest star in our sky. Its estimated diameter is five times that of our sun, with a luminosity of 160 times our sun. Regulus is 85 light years from Earth and has a magnitude of 1.3.
Beta Leo (Denebola)
Denebola, Leo's Beta star, is the easternmost of a prominent triangle of stars set to the east of Regulus and provides us with the Lion's tail. Denebola is a white class A (A3) dwarf (hydrogen-fusing) star of temperature 8500 degrees Kelvin. At a distance of 36 light years it is twice as far away and therefore dimmer to the eye. Magnitude is 2.14.
Gamma leo (Algieba)
To the eye, Algieba shines at mid-second magnitude of 2.61, but even a modest telescope under good atmospheric conditions will be able to see it. Gamma Leo is a birany system, one appearing at bright third magnitude (2.61), the other at bright fourth 3.5. The brighter is a class K (K1) giant with a temperature of 4400 Kelvin, the fainter a somewhat warmer (4900 Kelvin) class G (G7) giant, making it the yellower one. Distance from earth is 126 light years.
Delta Leo (Zosma)
ZOSMA . A star with two names, one Greek, the other Arabic. Zosma rides the back of Leo the Lion and is the fouth brightest star in the constellation. Lying only 58 light years away, Zosma shines with a luminosity 23 times that of the Sun. Magnitude is 2.56
Notable objects:

Messier M 65
Messier 65 is a bright spiral galaxy of stars 35 million light from Earth. It has very tightly wound spiral arms, a large central bulge, and well defined dust lanes, this galaxy is a member of a group of galaxies known as the Leo triplet. The faint blue smudges along the spiral arms of M65 are large clusters of bright, newly formed stars within the distant galaxy while the bright individual stars are foreground objects in our own Milky Way galaxy. Magnitude is 9.3.

NGC 3628
NGC 3628 forms a conspicuous group with M65 and M66, the Leo Triplet or M66 group. NGC 3628 is seen edge-on. The dust band, or belt, is obviously distorted and deformed in the outer regions of the galaxy. The reason for this deformation is evidently the gravitational interaction with its two bright neighbors, M65 and M66. Distance is 35 million light years, and magnitude 8.9

Messier M66
Discovered in 1780 by Charles Messier who described it as a nebula. Its light is very faint and it is very close to M 65. They both appear in the same field in the refractor. M66 is a dusty galaxy, with distorted spiral arms. The asymmetry in the spiral can clearly be seen in the image above. it is 35 million light years away and has a magnitude of 9.5.

Messier M 95
The barred galaxy M95 is a member of the Leo I or M96 group. It was one of the galaxies in the key project of the Hubble Space Telescope for the determination of the Hubble constant: the HST was employed to look for Cepheid variables and thereby determine this galaxy's distance. A preliminary result was obtained and published in 1996-97, and implies a distance of all the galaxies in the Leo I group of between 35 and 38 million light years. Magnitude of M 95 is 9.7.

Humankind
credits:
image: Leo map: wikipedia
en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Leo_(constellation)
image: M 65
www.ghg.net/akelly/galaxy.htmimage:
image: NGC 3628
members.cox.net/~sidleach/ngc3628.htm
image: M66: latinquaser
www.latinquasar.com/index.php?option=com_content&task=view&id=125
image: M95
www.ing.iac.es/PR/press/ing100.html


