Post by glactus on Feb 17, 2008 7:18:45 GMT
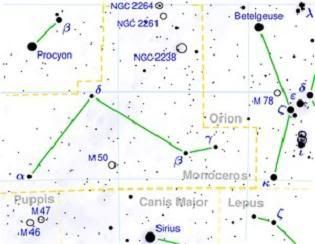
Monoceros is a faint constellation in the winter night sky, surrounded by Orion to the west, Gemini to the north, Cani Major to the south and Hydra to the east.
It is an almost invisible constellation, with only a few fourth magnitude stars. However, of all the constellations, Monoceros does have some very beautiful and stunning features to observe with the aid of even a small telescope.
Notable stars:
Alpha.Monocerotis
Alpha Monocerotis has a visual magnitude of 3.93, slightly brighter than Gamma Monocerotis, which has a visual magnitude of 3.98. Distance is 144 light years.
Beta Monocerotis
Beta Monocerotis is an impressive triple star system, the three stars form a triangle which seems to be fixed. The visual magnitudes of the stars are 4.7, 5.2 and 6.1. William Herschel discovered it in 1781 and commented it as "one of the most beautiful sights in the heavens". Distance is 175 light years.
Epsilon Monocerotis
Epsilon Monocerotis is a fixed binary, with visual magnitudes of 4.5 and 6.5. distance is 163 light years.
Notable objects:

NGC 2264: The Cone Nebula
The Cone Nebula (also known as NGC 2264) is an H II region, and was discovered by William Herschel in 1785. The nebula is located about 800 parsecs or 2,600 light-years away from Earth. It is part of the nebulosity surrounding the Christmas Tree Cluster. Magnitude is 4.7.

V838 Monocerotis
V838 Monocerotis is an unique object, probably a prototype of new class star erupting into a cool supergiant. The star "pulsed" away its outer layers in what can be described as a single flash - a sudden outburst - that occurred in January 2002, and reached a magnitude of 6.7 The emission of the surrounding cloud comes from the red supergiant star at the heart of this phenomenon. Distance from Earth is 20,000 light. years.

NGC 2237: Rosetta nebula
The Rosette Nebula is a large, circular H II region located near one end of a giant molecular cloud in this constellation. This Rosetta is about 50 light-years across and 4,500 light years from Earth. Star formation continues to occur in this nebula of gas and dust, so it should shine brightly for many millions of years to come. Magnitude is 7.0

NGC 2244
NGC 2244 is open cluster in the Rosetta nebula. The stars of this cluster formed from the surrounding gas only four million years ago, and emit light and wind that define the nebula's appearance today. Magnitude is 4.8 and distance from earth is 4,500 light years.

Trojan worlds
credits:
Monoceros mapn and sun map:Wikipedia
en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Monoceros
image: NGC 2264:cone nebula:An infrared Spitzer Space Telescope image: SIRT/NASA
en.wikipedia.org/wiki/NGC_2244
image: V838 monocerotis and location: wikipedia
en.wikipedia.org/wiki/V838_Monocerotis
image: NGC 2237 : Rosetta: astrotech
www.astrotech.it/italiano/gallery/rosetta_piero.JPG
image: NGC 2244: Wikipedia
en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Wikipedia:Featured_picture_candidates/NGC_2244


