Post by glactus on Feb 17, 2008 6:58:02 GMT
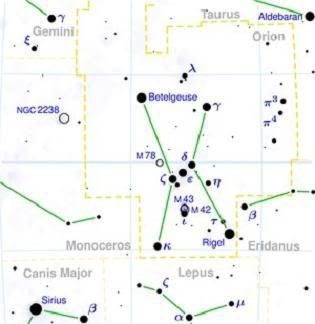
Perhaps second only to the Big Dipper in Ursa Major, the constellation of Orion is one of the most recognizable patterns of stars in the northern sky and is often referred to as "The Hunter". The constellation is extremely rich in bright stars and in deep-sky objects. Its brilliant stars are found on the celestial equator and are visible throughout the world, making this constellation globally recognized. In the northern hemisphere Orion is visible in the evening from November to April.
The constellation is also known as an "Amber" in countries such as the United Kingdom. Historically it has had other names, perhaps the earliest known is the Babylonian "Shepherd of Anu", corresponding to an apparent representation of the constellation Auriga or an element of it, as a shepherd's crook.
Notable stars:
á Ori (Betelgeuse)
Betelgeuse, at the right shoulder `of Orion, is a variable red star with a diameter larger than the orbit of Mars. Although it is the á-star, it is somewhat fainter than Rigel. Magnitude is 0.8 and distance from earth is 520 light years.
ã Ori (Bellatrix),
Bellatrixis at Orion's left shoulder, a blue supergiant shining at magnitude 1.6, it is the 22nd brightest star in the sky and 245 light-years from earth
â Ori (Rigel)
Invisible to the naked eye, Rigel is a B8 Ia,b supergiant, one that has already exhausted its core supply of hydrogen; at 17 solar masses, it shines with approximately 40,000 times the luminosity of the Sun, making it the most luminous star in our local region of the milky way. This star is 800 light years away and the magnitude is 0.12
ê Ori (Saiph)
Saiph, the star marking the right knee of Orion is of magnitude 2.1 and is a blue supergiant. Distance from earth is 720 light years.
Notable objects:

Messier M 42 the Orion nebula
The Orion Nebula, M 42, NGC 1976) is a diffuse nebula situated south of Orion's Belt. It is one of the brightest nebulae, and is visible to the naked eye in the night sky. M42 is located at a distance of about 1,500 light years away, and is the closest region of star formation to Earth. The M42 nebula is estimated to be 30 light years across. Magnitude is 4.0

IC 434
IC 434 is the bright background nebula against which the famous dark region called the Horsehead stands out. It is a long thin nebulous region running north to south near Alnitak, the eastern star of Orion's Belt. magnitude is 7.0 and distance from earth 1,300 light years.

The Horsehead Nebula
The Horsehead Nebula, also known as Barnard 33' in bright nebula IC 434) is a dark nebula in this constellation. The nebula is located just below Alnitak, the easternmost star of Orion's Belt, and is part of the much larger Orion Molecular Cloud Complex. It is approximately 1,500 light years from Earth, and is approximately 3.5 light years wide. Magnitude is 9.0

Messier M43
M43 is actually a part of the Great Orion Nebula, M42, which is separated from the main nebula by an impressive, turbulent dark lane. This diffuse nebula surrounds the irregular young "nebula variable" NU Orionis (HD 37061) It seems that M43 is excited to shine by this star, and contains its own, separate small cluster of stars which have formed in this part of the Orion nebula. Magnitude is 9.0 and distance 1,500 light years.

Horsehead
credits:
orion map: Wikipedia
en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Orion_(constellation)
image: Messier M42 the orion nebula in visible light NASA / ESA- Hubble
en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Image:Orion_Nebula_-_Hubble_2006_mosaic_18000.jpg
image: IC 434: telescopes
www.telescopes.cc/ic434.htm
image: The horsehead nebula: Wikipedia
en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Horsehead_Nebula
image: Messier M 43:deepskyobserving
www.deepskyobserving.com/Messier/M43.htm


