Post by glactus on Feb 17, 2008 6:44:23 GMT
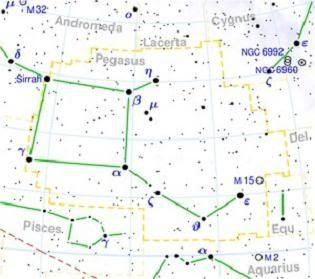
The constellation of Pegasus today represents the head and forequarters of the famous horse. It is a large constellation, the seventh largest in the sky, in terms of area. The horse is upside-down in the sky for northern hemisphere observers, with his head facing south, and it doesn’t take much imagination to see him prancing through the night sky. This constellation is home to the famous round galaxy NGC 7742, a gem of the sky, and the beautiful Stephan's Quintet.
Notable stars:
51 Pegasi
51 Pegasi is the first Sun-like star known to have an extrasolar planet, and the first evidence of atmospheric water vapour beyond the solar system. Magnitude is 5.99 and distance from Earth is 50.1 light years
Alpha Pegasi
Alpha Pegasi is the third brightest star in this constellation, and one of the four stars in the asterism known as the Great Square of Pegasus. It also has the traditional name Markab, which is a relatively average star nearing the end of its stellar evolution on the main sequence. Magnitude is 2.49 and distance from Earth is 140 light years.
Beta Pegasi
Beta Pegasi is a star with the traditional name of Scheat; confusingly, this name is also sometimes used for Delta Aquarii. Scheat is a red giant some 95 times as large as the Sun and has a total luminosity of 1500 times solar. It is also an irregular variable star, with brightness varying from magnitude +2.31 to +2.74. Distance from Earth is 199 light years.
Epsilon Pegasi
Epsilon Pegasi has the traditional name Enif. It is fairly average for an orange supergiant star, well into the later stages of its stellar evolution and as such may be considered a dying star. Enif likely only has a few million years left to go, although it is unknown whether it will explode in a supernova or die off as a rare neon-oxygen white dwarf. Magnitude is 2.38 and distance from Earth is 700 light years.
Notable objects:

NGC 7742
About 72 million light-years away in the constellation Pegasus, NGC 7742 is known to be a Seyfert galaxy - a type of active spiral galaxy with a center or nucleus which is very bright at visible wavelengths. Across the spectrum, the tremendous brightness of Seyferts can change over periods of just days to months and galaxies like NGC 7742 are suspected of harboring massive black holes at their cores. This beautiful color picture is courtesy of the Hubble Space Telescope Heritage Project. Magnitude is 12.4.

Stephan's Quintet
Stephan's Quintet is a visual grouping of five galaxies of which four form the first compact galaxy group ever discovered. The group was discovered by Edouard Stephan in 1877 at Marseilles Observatory, and is the most studied of all the compact galaxy groups. Magnitude is 14.8, and distance from Earth is 300 million light years.

NGC 7479
NGC 7749 is a Barred Spiral Galaxy (type SBb). . It has a very asymmetric spiral structure. The dominant features are the bright, long bar and the luminous western spiral arm. Supernova SN 1990U occurred in this galaxy. Distance from Earth is 105 million light years, and magnitude 11.6.

NGC 7331
NGC 7331 was among the earliest recognized spiral galaxies, and listed by Lord Rosse in his list of 14 "spiral or curvilinear nebulae" discovered before 1850. It is one of the brighter galaxies which is not included in Messier's catalog, and exposes a fine spiral structure despite its small inclination from the edge-on position. Magnitude is 9.5 and distance from Earth is 93 million light years.

Stephan's Quintet
credits:
Pegasus map: Wikipedia
en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Pegasus_(constellation)
image: NGC 7742: NASA
apod.nasa.gov/apod/ap030726.html
image: Stephan's Quintet:
chamorrobible.org/gpw/gpw-20050831.htm
image: NGC 7479: noao
www.noao.edu/outreach/aop/observers/n7479.html
image: image: NGC 7331:Spitzer-NASA
www.nasa.gov/lb/vision/universe/starsgalaxies/spitzer-062804_prt.htm


