Post by glactus on Feb 17, 2008 5:21:02 GMT
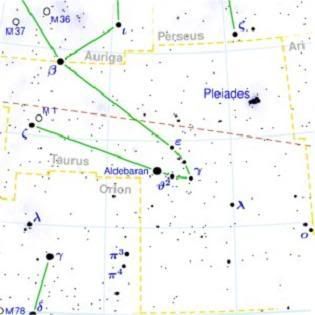
Taurus: Latin: 'bull', is one of the constellations of the zodiac. Around 4000 B.C., the Sun's position along the Zodiac on the first day of spring, (Vernal Equinox), was in Taurus, the Bull. So for many centuries Taurus was to be the first and most important constellation of the Zodiac. Some have suggested that Taurus may have been the first Zodiac constellation invented. It now sits large and prominent in the winter sky, between Aries to the west and Gemini to the east; to the north lie Perseus and Auriga, to the southeast Orion, and to the southwest Eridanus and Cetus.
Notable stars:
Alpha Tauri
Aldebaran from the Arabic: "the follower", (Alpha Tauri) is the brightest star in this constellation and one of the brightest in the night time sky. Because of its location in the head of Taurus, it has historically been called the Bull's Eye. Its name refers to the way the star follows the Pleiades star cluster in its nightly journey across the sky. Magnitude is .87 and distance from Earth is 65 light years
Beta Tauri
Beta Tauri is the second brightest star in the constellation with apparent magnitude 1.7. Relative to our Sun, this star is notable for a high abundance of manganese, but a paucity of calcium and magnesium. This star has begun to evolve away from the main sequence, becoming an orange giant. Distance from Earth is 131 light years.
Eta Turi (Alcyone)
Eta Tauri is the brightest star in the Pleiades open cluster and approximately 440 light years from Earth. The primary component, Alcyone A, is a blue-white B-type giant with an apparent magnitude of 2.85. It is an eclipsing binary, and the two components have a separation of 0.031 arcseconds, The binary star is orbited by three companions. Alcyone B and Alcyone C are both 8th magnitude white A-type dwarfs.
Atlas A
Atlas A is a triple star system also known as 27 Tauri. The primary component, Atlas A, is a blue-white B-type giant with an apparent magnitude of 3.62. It is a spectroscopic binary whose components have magnitudes of 4.1 and 5.6. The binary makes one orbit every 1250 days. Atlas also has a dimmer magnitude 6.8 companion, Atlas B, at a separation of 0.4 arcseconds. Distance from Earth is 381 light years.
Notable objects:

Messier M1 - The Crab Nebula
M 1, NGC 1952, Taurus A, is a supernova remnant and pulsar wind nebula in this constellation. The nebula was first observed in 1731 by John Bevis, and corresponds to a bright supernova that was recorded by Chinese and Arab astronomers in 1054. M1 is Located at a distance of about 6,300 light years from Earth. At the center of the nebula lies the Crab pulsar, a rotating neutron star, which emits pulses of radiation from gamma rays to radio waves with a spin rate of 30.2 times per second. Magnitude is 8.4.

Messier M 45 (the Pleiades)
The Pleiades, also known as M 45, or the Seven Sisters, is among the nearest to the Earth of all the open clusters, probably the best known, and certainly the most striking to the naked eye. The cluster is dominated by hot blue stars, which have formed within the last 100 million years.

Pleiades gas clouds
Astronomers estimate that the cluster will survive for about another 250 million years, when it will have dispersed due to gravitational interactions with the spiral arms of the galaxy and giant molecular clouds. Centre star magnitude is 15.5 to 16.0, and distance from Earth is 440 light years.

NGC 1514
Discovered by William Herschel on November 13th 1790. NGC 1514, An "irregular" planetary nebula lies in Taurus near the border of Perseus. The first peculiarity is the bright central star -- brighter, in fact, than the nebula around it, making the nebula itself somewhat difficult to see. Once found, NGC-1514 appears as an irregular 11th magnitude haze surrounding a 9.7 magnitude star. Gas is presumably expanding away from the larger star of the pair. Additional stars are found on either side of the nebula. Distance from Earth is 4,300 light years.

NGC 1514
credits:
Taurus map: Wikipedia
en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Taurus_(constellation)
image: Messier M 1 crab nebula: NASA:Wikipedia
en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Crab_Nebula
image: Pleiades: nasa.gov/apod
apod.nasa.gov/apod/ap060109.html
image: Pleiades: color: Spitzer:NASA/JPL-Caltech
upload.wikimedia.org/wikipedia/en/3/35/Pleiades_ir_nasajpl.jpg
image: NGC 1514: wikipedia
en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Image:NGC1514.jpg


