Post by glactus on Feb 17, 2008 5:12:50 GMT
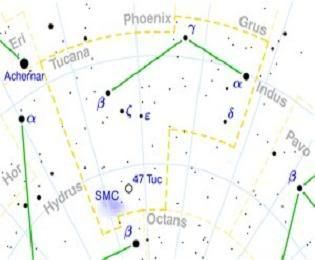
Tucana is named from the Toucan, a brightly colored South American bird with a very large, thick bill. Tucana was a collaboration between the Dutch navigators Keyser and de Houtman who charted the southern skies on a voyage to the East Indies, and Johann Bayer, an astronomer who cataloged and published their newly discovered star patterns in his 1603 sky atlas. Johannes Kepler, who formulated the three laws of planetary motion, and Giovanni B. Riccioli, who was the first to observe a double star, called it Anser Americanus, the American Goose. Tucana is its official name.
Notable stars:
Alpha Tucanae
The primary component, Alpha Tucanae A, is an orange K-type giant with an apparent magnitude of 2.87. It is approximately 199 light years from Earth. The system is an astrometric binary, which means that the companion star has not been directly observed, but its presence has been inferred from measuring changes in the proper motion of the primary. The orbital period of the binary system is 11.5 years.
Beta Tucanae
Beta Tucanae is a group of six stars which appear to be at least loosely bound into a system in this constellation. Three of the stars are luminous enough to have been given their own Bayer designations - b1 Tucanae through b3 Tucana. The system is approximately 140 light years from Earth with the two brightest stars, Beta-1 Tucanae and Beta-2 Tucanae having magnitudes of 4.56 and 4.53 respectively.
Gamma Tucanae
Gamma Tucanae is a yellow-white F-type giant with an apparent magnitude of +3.99 and approximately 71.8 light years from Earth.
Delta Tucanae
Delta Tucanae is a beautiful binary star
approximately 267 light years from Earth. The primary component, Delta Tucanae A, is a blue-white B-type main sequence dwarf with an apparent magnitude of 4.51. The companion star is of magnitude 9.3 and 7 arcseconds from the primary.
Notable objects:

The Small Magellanic Cloud
The Small Magellanic Cloud is a dwarf galaxy in orbit around the Milky Way Galaxy. It contains several hundred million stars. Some speculate that the SMC was once a barred spiral galaxy that was disrupted by the Milky Way to become somewhat irregular. It still contains a central bar structure. At a distance of about 200,000 light-years, it is one of the Milky Way's nearest neighbors. It is also one of the most distant objects that can be seen with the naked eye. Magnitude is 2.7

47 Tucanae
47 Tucanae is an ancient cluster of several million stars about 15,000 light years from Earth. The stars in 47 Tuc are about 10-12 billion years old, making them among the oldest stars in the galaxy. Near the centre of 47 Tuc, stars are so densely packed that solar systems like ours might well be disrupted by passing stars, and night skies might never be fully dark. Such clusters, with huge numbers of stars about the same age, are living laboratories for studies of the life, birth, and death of stars. Magnitude is 4.03

Blue stragglers
Blue straggler stars in the core of NGC 6397 formed from the merger of smaller objects. Located about 8,500 light years away from the sun, one is three times as heavy as the most masssive normal stars in the cluster, which suggests that it was born from multiple collisions. Magnitude is 4.6

Art Planets
credits:
Tucana map: Wikipdia
en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Tucana
image: Small Magellanic Cloud: newscientist.com
space.newscientist.com/article/dn10916-speeding-dwarfs-upset-galactic-family-picture.html
image: 47 Tucanae:science.psu.edu
www.science.psu.edu/alert/SALT8-2005.htm
image: Blue Stragglers: solstation.com
www.solstation.com/x-objects/bluestrag.htm


