Post by glactus on Feb 17, 2008 4:49:44 GMT
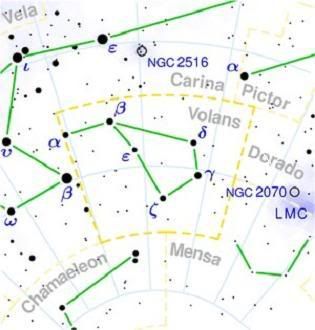
Volans, Latin: flying fish is a constellation of the southern sky. Since Volans was first described in the 17th century, there is no earlier mythology associated with it. This constellation was initially named Piscis Volans by Johann Bayer in his Uranometria of 1603. It has since lost its prefix and is thought to be inspired by sailors in the south seas, who reported seeing schools of flying fish gliding across the water for over distances of 400m.
Notable stars:
Alpha Volantis
Alpha (a Volantis) is a white A-type subgiant with an apparent magnitude of 4.00. It is approximately 124 light years from Earth.
b Volantis
Beta Volantis (b Volantis) is the brightest star of this constellation with a magnitudeof 3.77 and of spectral class K1III. Distance from Earth is about 108 light years.
Gamma Volantis
Gamma Volantis ( y Volantis) is a binary star in this constellation. It is approximately 142 light years from Earth. The primary component, designated y Volantis 2, is an orange K-type giant with an apparent magnitude of 3.78. Its companion, y Volantis 1, is a yellow-white F-type main sequence dwarf with an apparent magnitude of 5.68. The two stars are 14.1 arcseconds apart.
Epsilon volantis
Epsilon Volantis (eVolantis - the flying fish) is a triple star system in this constellation and approximately 642 light years from Earth. The primary component, Epsilon Volantis A, is a spectroscopic binary, classified as a blue-white B-type subgiant and has an apparent magnitude of 4.35. The binary system has an orbital period of 14.17 days. The binary's companion, Epsilon Volantis B, is 6.05 arcseconds away and has an apparent magnitude of 8.1.
Notable objects:

NGC 2442
This unusual barred spiral galaxy was discovered by Sir John Herschel who described one of its spiral arms as hook-like. Although not seen here, NGC 2442 appears to have a less massive, distant companion that is also distorted, and it seems likely that the two have had a close encounter in the recent past. If there are no further meetings, the forces that hold NGC 2442 together will restore the galaxy to a more symmetrical spiral form. However, much more likely is that the companion has been captured by the distorted spiral and will eventually be devoured by it, triggering a dramatic bout of star formation. NGC 2442 is about 50 million light years distant and its apparent magnitude is 11.2.

AM 0644-741
Resembling a diamond-encrusted bracelet, a ring of brilliant blue star clusters wraps around the yellowish nucleus of what was once a normal spiral galaxy in this new image from NASA's Hubble Space Telescope. The galaxy, cataloged as AM 0644-741, is a member of the class of so-called "ring galaxies." It lies 300 million light-years from Earth and has a magnitude of 13.6.

credits:
Volans map: wikipedia
en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Image:Volans_constellation_map.png
image: NGC 2442:starshadows
www.starshadows.com/gallery/display.cfm?imgID=132
image: AM 0644-741: hubble. apod.NASA/gov.
apod.nasa.gov/apod/image/0404/ringam_hst.jpg


