Post by glactus on Dec 31, 2011 0:19:53 GMT
The Gravity Recovery and Interior Laboratory (GRAIL) is an American lunar science mission in NASA's Discovery Program, which will use high-quality gravitational field mapping of the Moon to determine its interior structure. The two small spacecraft GRAIL A and GRAIL B were launched on 10 September 2011 aboard a single launch vehicle: the most-powerful configuration of a Delta II, the 7920H-10. GRAIL A separated from the rocket about nine minutes after launch, GRAIL B followed about eight minutes later. They will arrive at their orbits around the Moon 24 hours apart.

The launch of the Grail satellites
The science phase of the mission will last for 90 days. Following the science phase (or extended mission phase), a five-day decommissioning period is planned, after which the spacecraft will impact the lunar surface in about 40 days.The gravity mapping technique is similar to that used by Gravity Recovery and ClimatE Experiment (GRACE), and the spacecraft design is based on XSS-11.
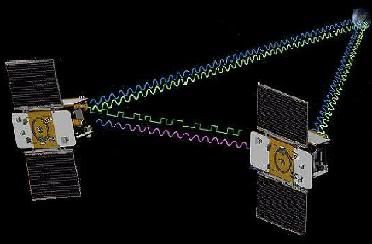
The Grail satellite configuration
Unlike the Apollo program missions, which took three days to reach the Moon, GRAIL will make use of a three- to four-month low-energy trans-lunar cruise via the Sun-Earth Lagrange poinT L1 to reduce fuel requirements, protect instruments and reduce the velocity of the two spacecraft at lunar arrival to help achieve the extremely low 50 km (31 mi) orbits with separation between the spacecraft (arriving 24 hours apart) of 175 to 225 km (109 to 140 mi).

Grail at lunar position
To see video of the Grail mission just click on the link below. Has sound. Full screen option bottom right
www.youtube.com/watch?feature=player_detailpage&v=1elSL-w1B8g

Credits: These are non copywrite images
Text by wikipedia
Video by Youtube

The launch of the Grail satellites
The science phase of the mission will last for 90 days. Following the science phase (or extended mission phase), a five-day decommissioning period is planned, after which the spacecraft will impact the lunar surface in about 40 days.The gravity mapping technique is similar to that used by Gravity Recovery and ClimatE Experiment (GRACE), and the spacecraft design is based on XSS-11.

The Grail satellite configuration
Unlike the Apollo program missions, which took three days to reach the Moon, GRAIL will make use of a three- to four-month low-energy trans-lunar cruise via the Sun-Earth Lagrange poinT L1 to reduce fuel requirements, protect instruments and reduce the velocity of the two spacecraft at lunar arrival to help achieve the extremely low 50 km (31 mi) orbits with separation between the spacecraft (arriving 24 hours apart) of 175 to 225 km (109 to 140 mi).

Grail at lunar position
To see video of the Grail mission just click on the link below. Has sound. Full screen option bottom right
www.youtube.com/watch?feature=player_detailpage&v=1elSL-w1B8g
Credits: These are non copywrite images
Text by wikipedia
Video by Youtube


