Post by glactus on Jan 10, 2011 11:07:38 GMT
The day may not be far away when an elevator attendant asks your preferred destination - low earth orbit (LEO) or geostationary orbit (GSO). Research is fast progressing in advanced countries on designing a space elevator, according to an Indian space expert.
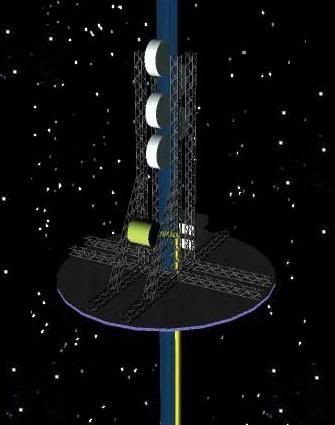
Concept (1)
"Space scientists and engineers are looking at the possibility of designing an elevator to travel into space. Indian research institutions are developing carbon nanotube composite fibre, nano epoxy and laser power beaming," A. Senthil Kumar, deputy head at the Vikram Sarabhai Space Centre (VSSC), told IANS in an interview.

Concept (2)
"The space elevator consists of a cable from an anchor in the ground to a counter weight located beyond geostationary orbit (GSO) that is 35,786 km away. A climber will move up on a carbon nanotube tether between earth and space."

Concept (3)
According to Kumar, once the infrastructure comes into position, the cost of carrying anything from earth to the GSO will be reduced to less than $250 per kg from the current $40,000 per kg.

Concept (4)
"A tall building on earth could be the anchor, from which a tether made of carbon nanotube composite fabric would extend to about 50,000 km towards the heaven, and the elevator would travel at 200 km per hour and reach the GSO in eight days,
Carbon nanotube has a tensile strength of 300 gigapascal whereas the required strength for space travel is only 130 gigapascal. The carbon nano fibres currently developed has tensile up to five gigapascal.
"The cable will be thickest at the top and taper down towards the earth. "Radiation, lightning, wind, meteors, space debris...but these are issues that can be dealt with,"

Space Elevator
Sourse and cedits: Press Trust of India

Concept (1)
"Space scientists and engineers are looking at the possibility of designing an elevator to travel into space. Indian research institutions are developing carbon nanotube composite fibre, nano epoxy and laser power beaming," A. Senthil Kumar, deputy head at the Vikram Sarabhai Space Centre (VSSC), told IANS in an interview.

Concept (2)
"The space elevator consists of a cable from an anchor in the ground to a counter weight located beyond geostationary orbit (GSO) that is 35,786 km away. A climber will move up on a carbon nanotube tether between earth and space."

Concept (3)
According to Kumar, once the infrastructure comes into position, the cost of carrying anything from earth to the GSO will be reduced to less than $250 per kg from the current $40,000 per kg.

Concept (4)
"A tall building on earth could be the anchor, from which a tether made of carbon nanotube composite fabric would extend to about 50,000 km towards the heaven, and the elevator would travel at 200 km per hour and reach the GSO in eight days,
Carbon nanotube has a tensile strength of 300 gigapascal whereas the required strength for space travel is only 130 gigapascal. The carbon nano fibres currently developed has tensile up to five gigapascal.
"The cable will be thickest at the top and taper down towards the earth. "Radiation, lightning, wind, meteors, space debris...but these are issues that can be dealt with,"
Space Elevator
Sourse and cedits: Press Trust of India


