|
|
Post by glactus on Oct 16, 2008 20:11:45 GMT
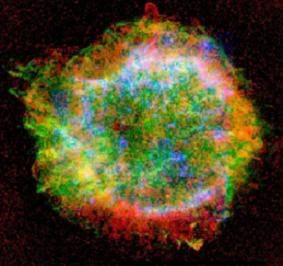 Cassiopeia A Cassiopeia A is a supernova remnant in the constellation Cassiopeia and the brightest extrasolar radio source in the sky. The supernova occurred approximately 11,000 light years away in the Milky Way. The expanding cloud of material left over from the supernova is now approximately 10 light years across. It is believed that first light from the stellar explosion reached Earth approximately 300 years ago but there are no historical records of any sightings of the progenitor supernova, probably due to interstellar dust absorbing optical wavelength radiation before it reached Earth Possible explanations lean toward the idea that the source star was unusually massive and had previously ejected much of its outer layers. These outer layers would have cloaked the star and reabsorbed much of the light released as the inner star collapsed. It is known that the expansion shell has a temperature of around 50 million degrees Fahrenheit and is travelling at more than ten million miles per hour. Cassiopeia A is the strongest radio source in the sky beyond our solar system, and was among the first discrete sources to be found.  Credits: This is a NASA imag |
|
|
|
Post by Andy Mac on Oct 16, 2008 21:42:28 GMT
Cassiopeia is definitely one of the most easily recognised constellation in the sky and home to many deep sky objects including M52, the Pacman nebula - and also a couple of nebulae called the Heart and Soul (IC1805 & IC1848) and shown in my poorly framed shot below:  |
|