Post by glactus on Jul 16, 2011 0:47:33 GMT
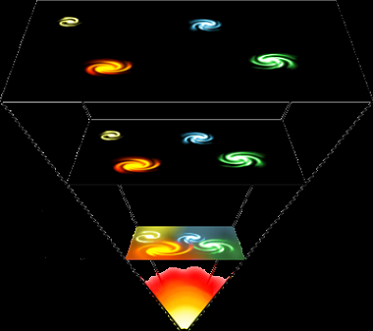
Expansion of the Universe
According to the Big Bang model, the universe expanded from an extremely dense and hot state and continues to expand today. A common analogy explains that space itself is expanding, carrying galaxies with it. The graphic scheme above is an artist's concept illustrating the expansion of a portion of a flat universe.
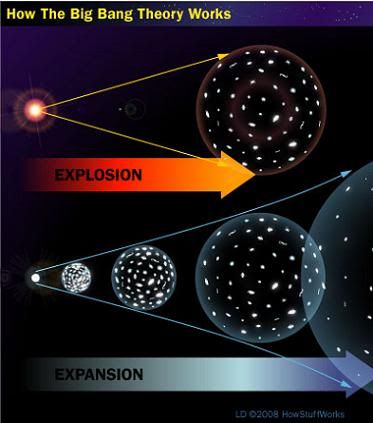
The explosion of the Universe
The Big Bang model, or theory, is the prevailing cosmological theory of the early development of the universe. The theory purports to explain some of the earliest events in the universe but not the absolute earliest state of things, or where it comes from. Our universe was once in an extremely hot and dense state that expanded rapidly a "Big Bang". There is little consensus among physicists about the origins of the universe itself (i.e. just as evolution seeks to explain our past only after the origin of life, the Big Bang theory explains only what happened after the uncertain origin of the universe.
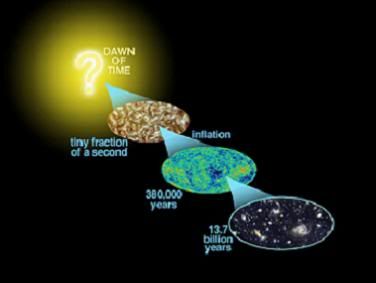
The three stages of expansion
What is clear is that the Big Bang caused the young universe to cool and resulted in the present diluted state that continues to expand today. Based on the best available measurements as of 2010, the original state of the universe existed around 13.7 billion years ago, which is often referred to as the time when the Big Bang occurred. The theory is the most comprehensive and accurate explanation supported by scientific evidence and observations.
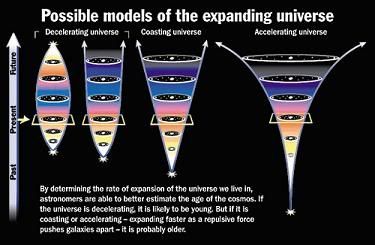
Acceleration of the Universe
If the distance between galaxy clusters is increasing today, everything must have been closer together in the past. This idea has been considered in detail back in time to extreme densities and temperatures, and large particle accelerators have been built to experiment on and test such conditions, resulting in significant confirmation of this theory. On the other hand, these accelerators have limited capabilities to probe into such high energy regimes.
There is little evidence regarding the absolute earliest instant of the expansion. Thus, the Big Bang theory cannot and does not provide any explanation for such an initial condition; rather, it describes and explains the general evolution of the universe going forward from that point on.
Also There are astronomers who find difficulty in explaining why massive galactic structures exist so close to the Bid Bang. Structures that themselves would only grow to that size by consuming other galaxies, a process that itself, in some cases, would have taken many billions of years, and leading many to speculate that there was no Big Bang at all, just two Universe's in collision. Maybe the James Webb telescope will be able to help us with that theory.
Looking at the Big bang
Credits; These are non copywrite mages
Text by wikipedia/Glactus
Telescope in avatar: Meade 16" LX 200
Astronomer in avatar: Glactus