Post by glactus on Feb 17, 2008 4:55:55 GMT
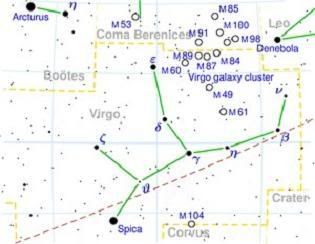
Virgo is the 6th sign of the zodiac; Lying between Leo to the west and the Libra to the east, and can be easily found through its brightest star, Spica.
The sun passes through this constellation from late september to the end of october. It is the second largest constellation in the sky (the largest is Hydra). The most outstanding Virgo Supercluster of galaxies is located on the northern border of Virgo reaching into the neighbouring constellation of Coma Berenices. Although this supercluster is 65 million light years away, the brightest galaxies can be located with small telescopes as faintly glowing patches of light.
Notable stars:
Alpha Virginus-Spica
The name Spica derives from Latin - spica virginis "Virgo's ear of grain" (usually wheat). Spica is the brightest star in the constellation, and one of the brightest stars in the nighttime sky. It is believed to be the star that provided Hipparchus with the data which enabled him to discover precession of the equinoxes. Spica is also the brightest of the rotating ellipsoidal variables. Its apparent magnitude varies between 0.92 and 1.04, with a period of 4.0142 days. This slight dip in magnitude is barely noticeable visually. It is also a variable of the Beta Cephei type. Distance from Earth is 280 light years.
Beta Virginis
b Virginis is a star with the traditional name Zavijava (also Zavijah). Despite being the beta star of this constellation, it is only the fifth star in order of brightness. Physically, Beta Virginis is larger and more massive than the Sun, and is comparitively metal-rich. That is, it has a higher preponderance of elements heavier than helium. Since it is close to the ecliptic, it can be occulted by the Moon and (very rarely) by planets. Apparent magnitude is 3.61 and distance rom Earth is 35.9 ligth years
Gamma Virginis
Gamma Virginis is a binary star, consisting of two stars of approximately equal apparent magnitudes 3.48 and 3.50, and of spectral type F0V. With an orbital period of 168.68 years, this star is and as easy object for amateur astronomers, but the smaller apparent distance between the stars requires a larger telescope.. The star system has a combined apparent magnitude of 2.9.and lies 32 light years away from our Sun.
Delta Virginis
Delta Virginis is a red giant with the traditional name of Auva. It has a spectral type of M3-III, and a magnitude of 3.38, bright enough to be seen with the naked eye. Auva is classified as a semi regular variable star and its brightness varies from magnitude 3.32 to 3.40. It is also a possible binary, as an 11th magnitude star is located only 80 arcseconds from it. This type K dwarf is believed to have an orbital period of over 200,000 years, but this has not been confirmed. Distance from Earth is 202 light years.
Notable objects:

Messiere M 58
Messier M58, also known as NGC 4579 is a barred spiral galaxy located approximately 68 million light-years from Earth. It was discovered by Charles Messier in 1779 and is one of the brightest galaxies in the Virgo Cluster. Two supernovae, SN 1988A and SN 1989M, have been observed in M58. Magnitude is 10.5

Messier M 61
Messier M61, also known as NGC 4303, is a spiral galaxy discovered by Barnabus Oriani on May 5, 1779 and is one of the larger members of the Virgo Cluster with five supernovae observed in its huge structure, the most recent in 2006. Apparent magnitude is 10.2 and distance from Earth is 60 million light years.

Messier M104 Sombrero
The Sombrero Galaxy, also known as M104 or NGC 4594) is an unbarred spiral, having a bright nucleus, an unusually large central bulge, and a prominent dust lane in its inclined disk. The dark dust lane and the bulge give this galaxy the appearance of a sombrero. The Sombrero has an apparent magnitude of 9.0, making it a galaxy that can easily be seen with amateur telescopes. The large bulge, the central supermassive black hole, and the dust lane all attract the attention of professional astronomers. This beautiful super giant structure is 11 times bigger than the Milky Way, has a diameter of 50,000 light years, and harbors more than a trillion suns. Distance from Earth is 37 million light years.

Messier M90
Messier 90, also known as NGC 4569) is a spiral galaxy discovered by Charles Messier in 1781. It has tightly wounded, smooth bright spiral arms, which appear to be completely "fossil", meaning that currently no star formation appears to be taking place, with the only exception of the inner disk region, near the darker dust lanes. Distance from Earth is about 60 million light-years and apparent magnitude is 10.3.

The Sombrero
credit
Virgo map: Wikipedia
en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Virgo_(constellation)
image: Messier M 58: Spitzer Space Telescope en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Messier_58
image: Messier M 61: noao.edu
www.noao.edu/outreach/aop/observers/m61blocks.jpg
image: Messiere M104 Sombrero
www.astrooptik.com/Bildergalerie/Lulin1m/m104_m.jpg
image: Messier M 90: seds.lpl.
seds.lpl.arizona.edu/messier/Pics/Jpg/m90siegelman.jpg


